Potatoes are pretty popular in the United States. It is estimated that the average person in the United States consumes about 125 pounds of potatoes or potatoes-related products per year. Potatoes are pretty nutritious, consisting of about 18% of starch and 2 % of proteins. In addition, they provide cheap amounts of carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. These are some of the reasons why they are highly consumed.
The growth of potatoes requires adherence to certain conditions to maximize their productivity. Stats have indicated that they give better yields during warmer seasons. On the contrary, potatoes do not do well during the cold seasons since they cannot weather well in frost.
Planting and Growing of Potatoes
When planning to grow potatoes, there are certain factors to consider since the endeavor requires various measures at various stages of the plant. The measures are end-to-end and should be considered stepwise for greater yields.
Potato varieties: There are several varieties of potatoes that one can choose from when planting. They include:
- Red LaSoda
- Red Pontiac
- White Kennebec
Plant preparation: When planning to plant potatoes, it is critical to prepare in advance to avoid missing out on their possible planting times, which is significant in determining the plant’s yield. As such, acquiring certified seeds a few weeks before planting time is highly recommendable. At the same time, one should exercise caution since acquiring the seeds from any source (such as grocery stores) may acquire those treated with sprouting inhibitors.
Note that the right time to plant potatoes in North and South Texas is basically between dates 10 and 20 in February (typically, the middle of February). It is expected that the potato seed should yield about four to five pounds of potatoes.
The significant reason why it is advisable to acquire the potato seeds in advance is to ensure that they have sprouted before the actual planting dates. This factor is crucial since it helps reduce the number of days the plant needs to mature for harvest.
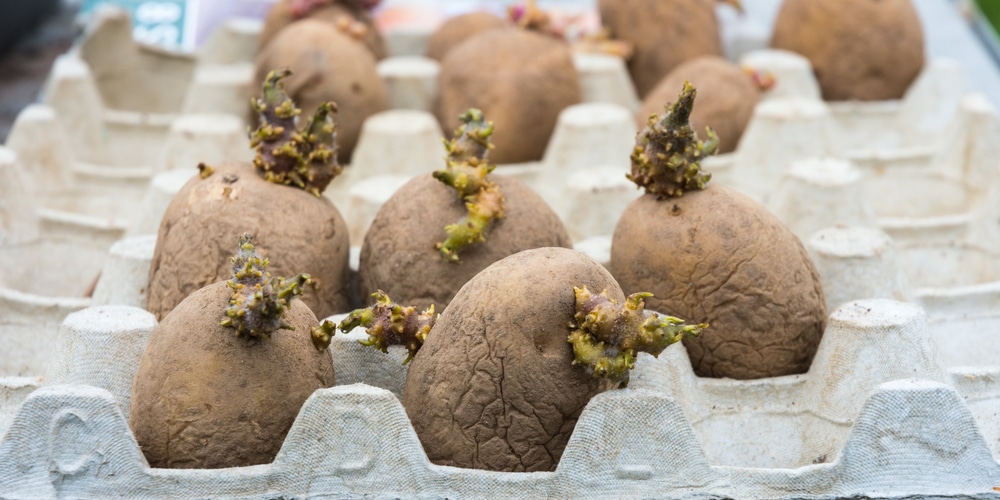
How to pre-sprout potato seeds
The process is vital in enabling the development of their shoots before actual planting and involves laying them in a cardboard or tray lined with a newspaper. Ensure to spread them in a single layer without allowing them to contact each other.
When sprouting them, it is vital to place them with no interference, more crucially, where they will be for the better part of their time without moving them. Moreover, they should be in a place with sufficient warmth since cold is a great hindrance to sprouting. With time, the potato eyes will begin producing the sprouts.
The sprouts should only be left to grow about ¾ to 1inch length; otherwise, they should be cut to remain in that length. Afterward, they should be allowed to dry a little bit. The next step involves dusting them using dusting sulfur, ensuring to leave them for another day. The plants are now ready for planting.
Actual Planting
Planting involves placing the potato sprouts in about six to eight width and depth furrows. Ensure to space the potato sprouts about ten inches apart to give their yields space to grow and multiply. Afterward, cover them with enough but not too much soil.
Within three to four weeks, the shoots or sprouts will appear above the soil, during which it is advisable to add more soil. They will be ready for harvesting in about three to four months, indicated by drying and yellowing of the tops.
Planting Potatoes in Texas: Hardiness Zones
When planting potatoes in Texas, it is essential to know the hardiness zone of the specific location since Texas has geographical differences that vary significantly. As indicated, potatoes only do well when grown in warm weather. Similarly, north and south Texas tomato planting dates compare with potato planting since tomatoes also do well during warm seasons.
The following table indicated the various hardiness zones in Texas that one should consider before planting potatoes or tomatoes.
| Texas GardeningZones | USDA HardinessZones | Average Min Temp (F) |
| Zone 1 | Zone six | -10F – 0 F |
| Zone 2 | Zone seven | 0F – 10 F |
| Zone 3 | Zone Eight | 10F – 20 F |
| Zone 4 | Zone Nine A | 20F – 25 F |
| Zone 5 | Zone Nine B | 25F – 30 F |
When to Plant Potatoes in Texas: Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to know the proper requirements and dates for planting potatoes in Texas. Typically, these factors are critical in enhancing appropriate crop yield. If ignored, the plants may encounter difficulties and yield a few small potatoes.