St. Louis is an independent city in Missouri, and it sits on a 62 square land area with about 4.1 square miles of water which sums up the total to about 66 square miles. St Louis features a variety of terraces and hills that range from 90 to 180 feet above the Mississippi river level. A part of St. Louis entails shallow valleys, low hills, rolling prairies, vast floodplains created by both Missouri and Mississippi rivers. And if you are looking for sinkholes, you can find them in the south downtown area; however, almost all of them are sealed. You can also get most springs near the riverfront.
As much as talking about popular St Louis sites is fun, that is not our topic of discussion today. This article will tackle all there is to know about the climatic zone of St Louis, MO.
What climatic zone is St. Louis, MO in?

Two different climates impact St. Louis climatic and weather conditions: humid subtropical and humid continental. Summers are hot and humid, and winters are bitterly frigid. Residents may be exposed to the chilly winds from the Arctic and the warm, moist tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico. In the city, there are four seasons:
- Spring (March to May): It’s the wettest season among the four, and it can include winter storms and severe tornadoes.
- Summer (May to September): It’s usually hot and humid. The temperatures of summer might hit highs of about 80 to 90 degrees.
- Fall (October to December): Fall is characterized by mild and sunny weather. However, it does present occasional rainfall.
- Winter (December to February): Presents cold weather and might cause one to two significant snowstorms.
St Louis, MO is located in USDA Zone 6, which is among one of the 13 climate hardiness zones found in the US.
What are hardiness zones?
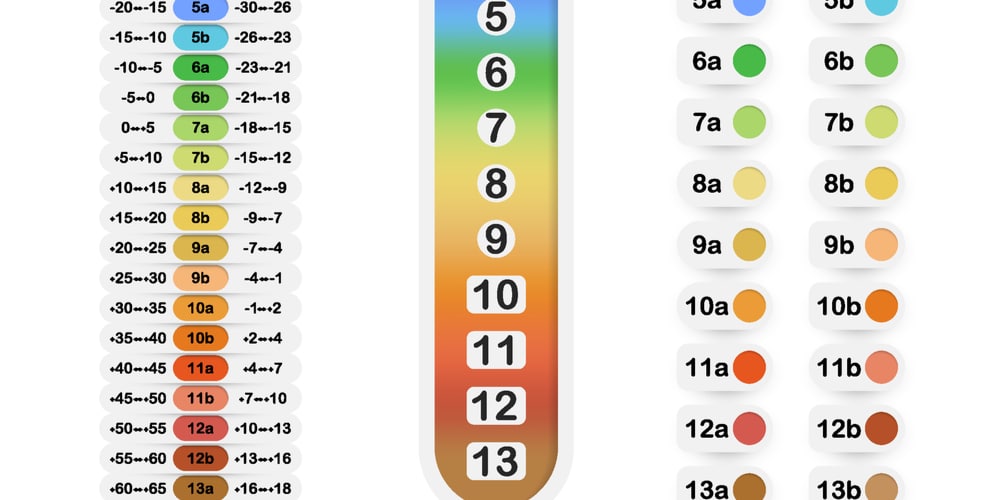
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides Canada and the US into 13 zones based on the average annual lowest winter temperature. Throughout the winter, all zones are 10 degrees hotter or cooler than the one beside them, with Zone 1 being the coolest and Zone 13 becoming the hottest.
This generally follows a north-to-south direction, but this isn’t always the case. Lakes, mountains, desert geography, and urban heat island factors can result in temperature variations between various zones within a few miles from each other at similar latitudes.
What specific zone is St Louis found in?
Each USDA Zone reflects a region with the lowest average winter temperatures in the system. The colder the part, the lesser the USDA Zone designation. However, a plant’s capacity to thrive is affected by elements other than temperature; the USDA Zone system is an excellent place to begin for most gardeners.
Missouri is split into four planting zones: 5b towards the northern regions, 6a and 6b at the center, and 7a in the south. The warmer growth zone of 7a is found in a tiny area of the state’s southeast corner.
All hardiness zones are split into two subsets; St Louis Mo is found in zone 6, meaning it has two subset zones which are 6a and 6b. Each subset zone has a difference of 5, this means :
- Zone 6: This zone features an average temperature of -10 to 0F.
- Zone 6a: The lowest average temperature from this subzone is -10degrees to -5degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 6b: The lowest average temperature under this subzone is -5degrees to 0F.
The zone and subgroup ranges are determined by the average lowest temperature for the cold season. Because colder temperatures sometimes happen, the temperatures may not always fall within this range.
Why is it essential for st Luis, MO citizen to understand their zone
Understanding your local climate and hardiness zone allows you to match the growth season, rainfall schedule and intensity, and average temperature to guarantee the plants you’re contemplating growing are suitable for the location.
What Climate Zone is Saint Louis, MO in?: Conclusion
You might think that knowing the climate zones only favors farmers or gardeners, but even commoners can benefit from this knowledge. Understanding the climate zones helps you prepare for weather and climate patterns changes. For example, it can help you determine the cold seasons and get extra jumpers or fit your home with house warming solutions and vice versa.
You may also be interested in: Best time of year to plant grass?