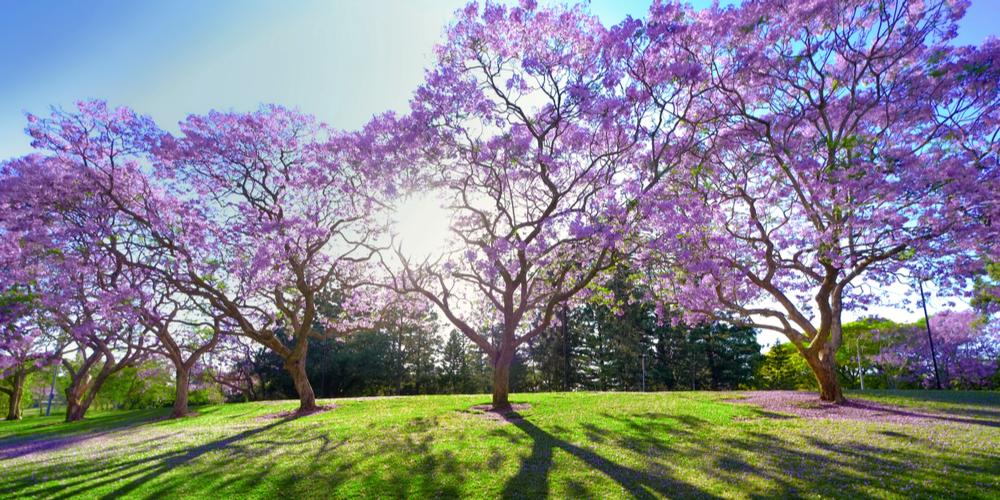
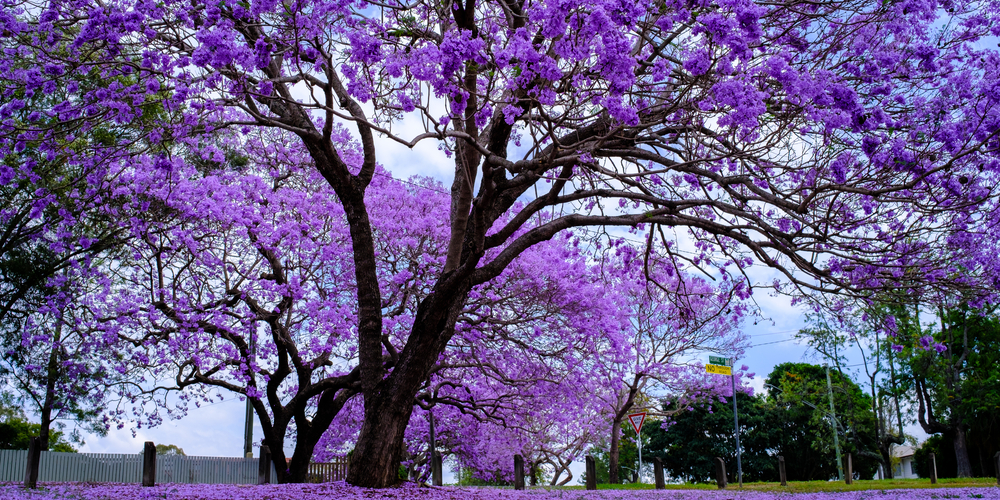
With its lush canopy shaped like an inverted umbrella, the Jacaranda Tree makes an excellent shade tree. It is a fast grower in the tropical environment and can reach heights up to 50 feet tall.
Aside from being tall growers, these trees also tend to spread, so consider the horizontal space you have in your yard before planting. It gains and grows approximately ten feet during its first few years. However, outside its ideal habitat, this tree’s growth is considerably slower.
Prized for its spectacular blue-violet flowers that can surely make any landscape pop with color, the Jacaranda Tree is a favorite landscaping plant in warmer climates. It’s often one of the first choices in terms of ornamental trees, and we can see why.
The Jacaranda Tree, also called Black Poui or Blue Jacaranda, is a native of South America, specifically Argentina and Bolivia but it has become naturalized in many other parts of the world, including Australia, Hawaii, Chile, Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, and Zambia. Today, it can also be found in the southern United States, specifically in California, Arizona, Texas, and Florida.

| Botanical Name | Jacaranda Mimosifolia |
| Common Name | Jacaranda Tree, Black Poui, Blue Jacaranda |
| Plant Type | Perennial |
| Flower Color | Violet, Blue-purple |
| Size When Mature | 300-600 inches |
| Bloom Time | Spring and Summer, Fall |
| Sun Requirements | Full Sun |
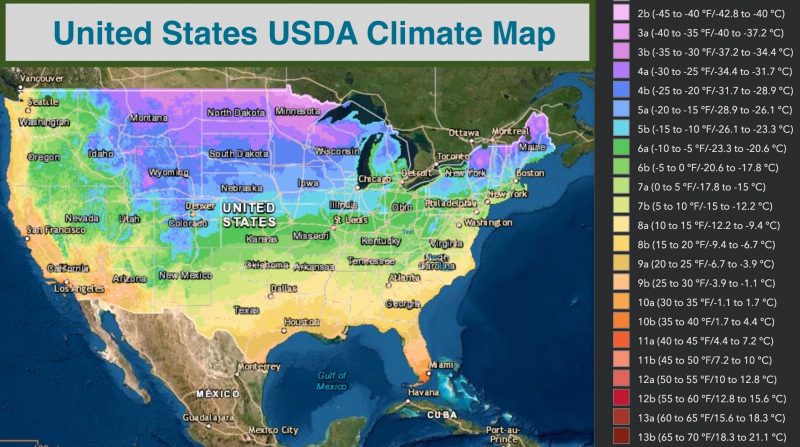
| USDA Hardiness Zones | 10 – 11 |
| Soil PH Range | 5.5 – 8.0 |
| Soil Type | Sandy, Rich, Well-draining |
| Water Needs | Low |
| Native Area | Northwestern Argentina and Southern Bolivia, South America |
What You Need to Know About Jacaranda Tree
The Jacaranda Tree blooms from late spring to early summer with lavender-blue flowers that emit a freshly sweet fragrance. However, these blooms can be messy as they fall and carpet the ground beneath the tree. Despite this, the tree is still widely planted in public parks and gardens because of its beautiful flowers.
Withered flowers may also produce a foul and pungent smell. Following this, interesting bean-like seed pods that hang from the branches soon appear. The pods are brown in color and measure about one to three inches wide.
The tree’s leaves are green, fern-like, compound, and arranged in pairs along the stems that are about 17 inches long. It has a smooth, gray bark that becomes corky as the tree matures.
That said, although the tree is drought and heat tolerant, it requires a bit of maintenance. Its messy flowers and fruits can be a problem in some areas, so it’s best to plant them where they won’t cause any inconvenience.
But aside from that, this tree is easy to grow and doesn’t require much pruning or fertilizer. Some seasonal pruning might be necessary to prevent the tree from getting too big for its location.
How to Care for Jacaranda Tree
Here’s everything you need to know about growing and caring for a thriving Jacaranda Tree:
Light
When it comes to Jacaranda Tree care, the most important thing to remember is that this tree needs full sun. It is absolutely necessary for this tree to receive at least six to eight hours of sun every day.
Smaller trees can tolerate partial shade, but they will not bloom as abundantly as those that are grown in full sun. Young plants can be grown indoors and should ideally be placed in a sunny spot near a window. Lack of sunlight may cause the plant to become leggy and produce fewer blooms.
Water and Soil Needs
When it comes to soil, the Jacaranda Tree is not too fussy. It will grow in most types of soil as long as it is well-drained. It grows best in slightly acidic soil with pH levels of 5.5 to 8.0.
This tree cannot tolerate wet or soggy soils, so make sure the planting site has good drainage. If your soil is heavy, mix in some sand or organic matter to improve drainage. If your soil has poor drainage and is water-logged, your tree is more susceptible to root rot and mushroom root rot.
This gentle giant is drought-tolerant once established, but young trees will need regular watering during their first few years. Water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep roots. This is the secret to making them grow fast during their forming years.
Established trees can dry out between watering, and they should only need to be watered once or twice a week, depending on the weather conditions. Tree roots typically grow about two feet deep, so make sure to water deeply enough to reach them.
Temperature Requirements
Jacarandas are sub-tropical trees and will thrive in environments with warm weather and long, hot summers. They can tolerate some cold but still prefers heat and humidity. These trees are hardy in USDA Zones 10 to 11.
Fertilizer
The best fertilizer to use on a Jacaranda Tree is a slow-release granular fertilizer. It is not a heavy feeder and requires little to no fertilizer once it has become established. You may feed your tree just once a year, preferably during early spring. Annual feeding of a 10-10-10 nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium fertilizer will give your tree the boost it needs.
Common Diseases
Aphids and scales are common pests that may infest your Jacaranda Tree. They do damage by sucking the sap from the leaves, causing discoloration, stunted growth, and deformed leaves. These pests also produce a sticky substance called honeydew that can attract ants and promote the growth of sooty mold.
Jacaranda trees are also susceptible to winged sharpshooters, which invade the tree through the leaves. These insects carry bacteria that can cause bacterial leaf scorch in the trees. The bacteria prevents the tree from obtaining the water it needs. Watering it as often will only prolong the tree’s life, but unfortunately, there is no cure for the disease.
These trees are also vulnerable to root rot and mushroom rot if they are grown in wet or poorly-drained soils. These diseases have no cure and will eventually kill the tree, so it is important to make sure the planting site has good drainage.
With that being said, preventive measures such as proper care and maintenance can go a long way in keeping your Jacaranda Tree healthy and disease-free.
Jacaranda Tree Propagation
There are many various ways to propagate this tree. You may choose to plant the seeds or use stem cuttings. Propagating via cuttings is preferable since your plant will bloom much sooner than one produced from a seed. Grafting is another option, but this may not be as friendly to beginners.
When propagating via cuttings, you may use either softwood or hardwood cuttings. Cuttings should be taken from a healthy plant that is at least two years old.
- First, you will need to prepare your cutting tools. Make sure your pruning shears are sharp and sterilized with rubbing alcohol to prevent the spread of diseases. You will also need a container filled with sterile potting mix.
- Next, take your cutting from the Jacaranda tree. Cuttings should be 4-6 inches long and taken from the tips of the branches. Cut at an angle and use the leaf nodes as your guide when cutting, making sure to include 2-3 nodes in your cutting.
- Remove the bottom leaves of the cutting, leaving only the top leaves intact. Dip the cut end of the cutting into rooting hormone and then plant it in your container of potting mix. Be sure to firm the mix around the cutting to secure it in place.
- Water your cutting well, and then place it in a location with indirect sunlight and high humidity. A propagation dome or clear plastic bag can create the humid environment your cutting needs to root.
- Cuttings will usually take 4-8 weeks to root. Once roots have developed, you may transplant your cutting into a larger pot or your garden, following the growing conditions mentioned above.