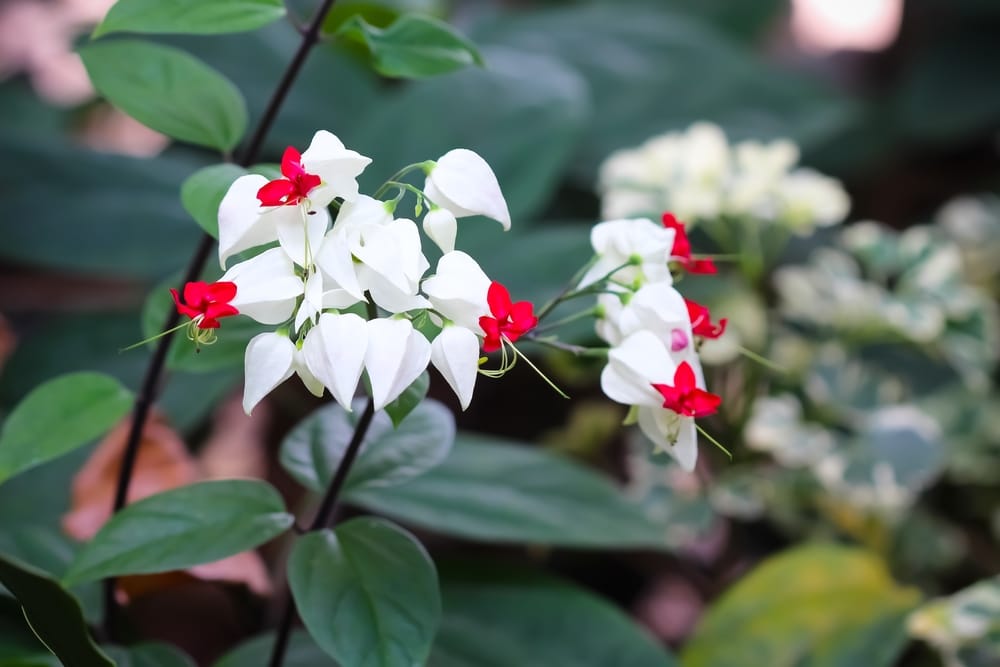
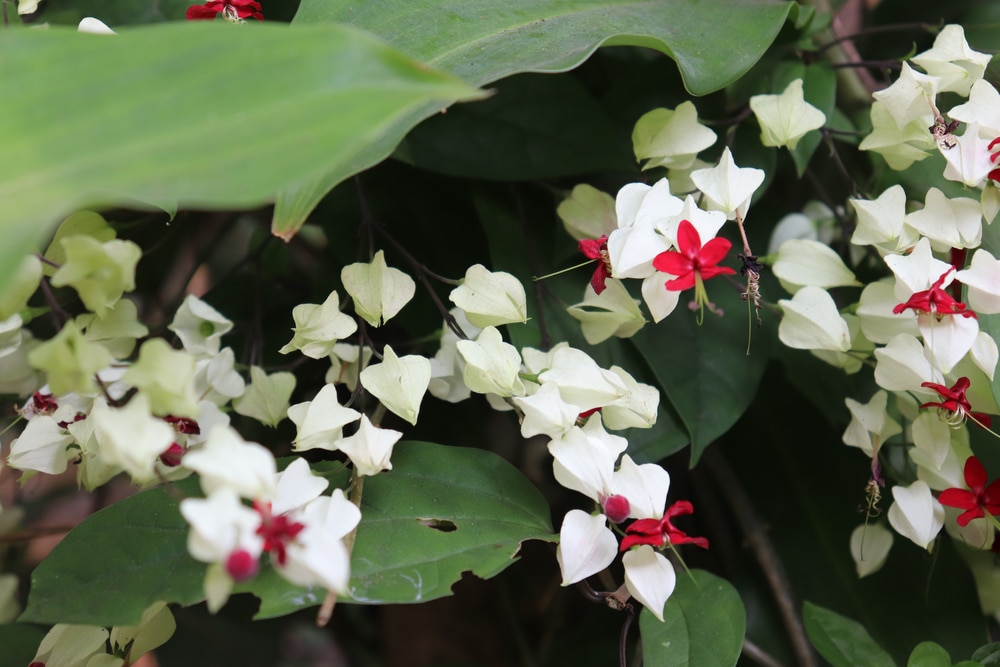
The Bleeding Heart Vine is a beautiful but notoriously finicky plant. Growing it can be a challenge, but the rewards are definitely worth it. With cascading clusters of pink or white heart-shaped flowers, this fast-growing vine can add a dramatic touch to any garden. But to keep your Bleeding Heart Vine healthy and blooming, there are a few things you need to know.
| Botanical Name | Clerodendrum Thomsoniae |
| Common Name | Bleeding Heart Vine |
| Plant Type | Perennial |
| Flower Color | Clusters of heart-shaped flowers that can come in either red, pink, yellow, white, or orange color |
| Size When Mature | 120-180 Inches |
| Bloom Time | Summer |
| Sun Requirements | Partial to Full Sun |
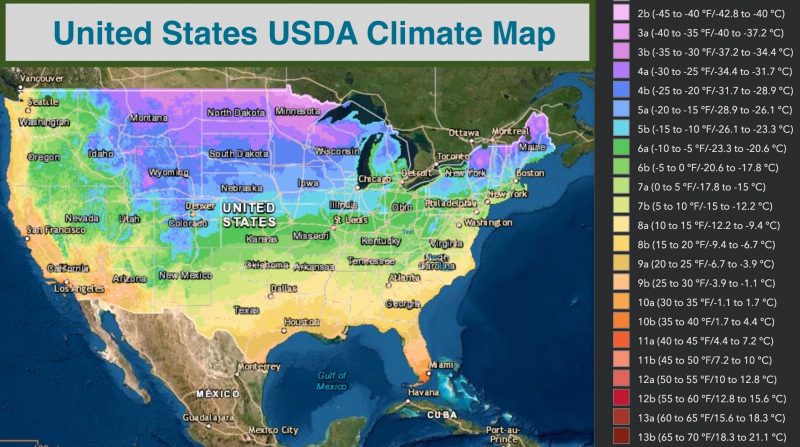
| USDA Hardiness Zones | 9 – 12 |
| Soil PH Range | 6.1 – 6.5 |
| Soil Type | Acidic, well-draining |
| Water Needs | Medium |
| Native Area | Africa |
What You Need to Know About Bleeding Heart Vine
The Bleeding Heart Vine is a fast-growing, semi-deciduous vine native to Africa. It can grow 10-15 feet in height and produces clusters of different colored heart-shaped flowers during summer. The flower color can be either red, pink, yellow, white, or orange.
Additionally, it has attractive oval-shaped leaves that are dark green and glossy. The leaf’s edges are smooth and pointed at the end, giving it a serrated look.
Despite the intimidating look and name of the plant, the Bleeding Heart Vine is actually relatively low-maintenance that is easy to care for. It is a drought-tolerant plant that can adapt to different types of soil.
However, the plant is toxic to humans and animals if ingested, so taking extra care while handling it is necessary. Keep pets and small children away from the plant to avoid any accidents.
How to Care for Bleeding Heart Vine
Here’s everything you need to know about growing and caring for a thriving Bleeding Heart Vine:
Light
Growing best in partial shade or dappled light, the Bleeding Heart Vine is a versatile plant that can adapt to various lighting conditions. It will tolerate full sun as long as you provide enough moisture to prevent the leaves from scorching and wilting. A minimum of four hours of indirect sunlight per day is ideal.
Water and Soil Needs
The best way to water your Bleeding Heart Vine is by giving it at least one inch of water per week. To ensure the plant gets enough water, check the soil regularly. It should be moist but not soggy. Only water the plant when the top few inches of soil are dry.
As for soil, the Bleeding Heart Vine is not picky and will do well in most types of soil as long as it is moist and well-draining, with a pH range of 6.1-6.5. To increase or decrease the soil’s acidity, you can add agricultural lime or sulfur, respectively. Additionally, adding a layer of organic compost to the planting area will help improve drainage and retention.
Temperature Requirements
The ideal temperature for Bleeding Heart Vine is between 55-75 degrees Fahrenheit. The plant can survive in USDA zones 9-12. While it can tolerate colder temperatures, it may start to show some temperature stress when soil temperatures reach below 45 degrees Fahrenheit.
Fertilizer
The best fertilizer to use on a Bleeding Heart Vine is a slow-releasing balanced fertilizer. This ensures that the plant gets the nutrients it needs without being overloaded. Too much nutrients and giving it to the plant all at once can actually do more harm than good. Feeding during the growing season, with a 2-3 month break during winter, is ideal.
Common Diseases
The biggest threat to your Bleeding Heart Vine is powdery mildew and root rot. These two diseases are often caused by too much moisture and humidity. When detected early on, they can be treated with a fungicide. However, if left unchecked, these diseases can be fatal for the plant.
Bleeding Heart Vine Propagation
Propagating the Bleeding Heart Vine is relatively easy and can be done through stem cuttings or serpentine layering.
To propagate through stem cuttings, take a four to six-inch cutting from a healthy plant and remove the bottom leaves and plant it in moist soil. You can dip the cutting in rooting hormone to help encourage growth. Cover the pot with plastic wrap to create a humid environment and place it in indirect sunlight. The cutting should root within four to six weeks.
Serpentine layering is another easy way to propagate the Bleeding Heart Vine. To do this, bend a stem to the ground and cover it with soil. The stem will then produce roots where it touches the ground and can be cut away from the mother plant after six to eight weeks.
Once your plant has rooted, you can transplant it to a pot or garden bed. Be sure to space the plants about two feet apart so that they have room to grow.
You May Also Like: What Plants Go Well With Hosta?