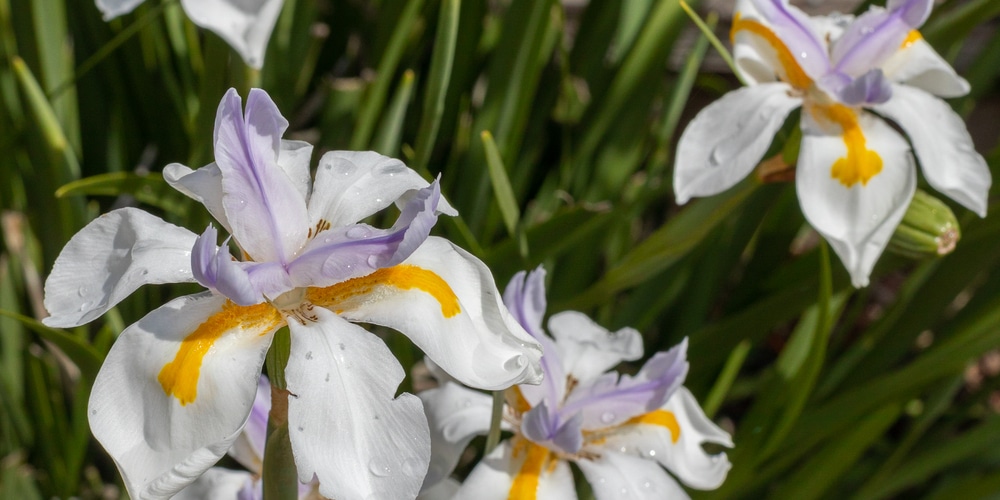
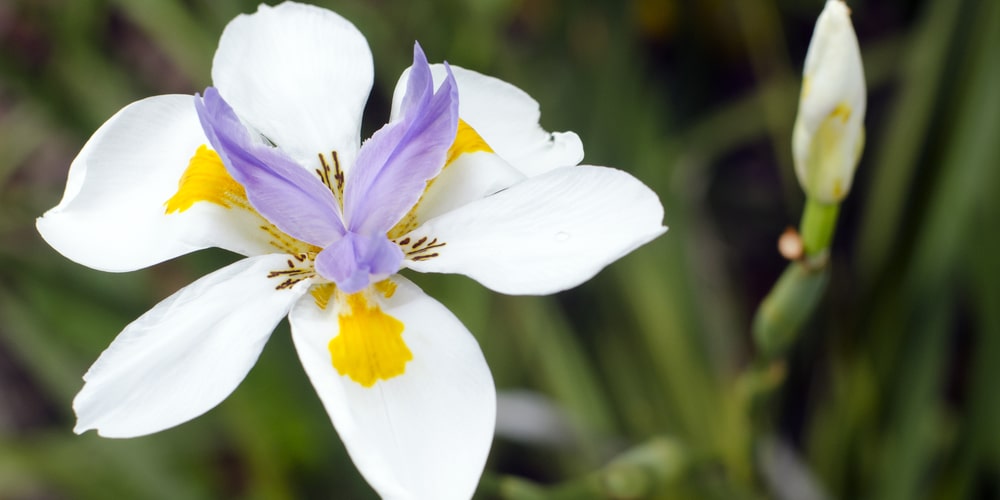
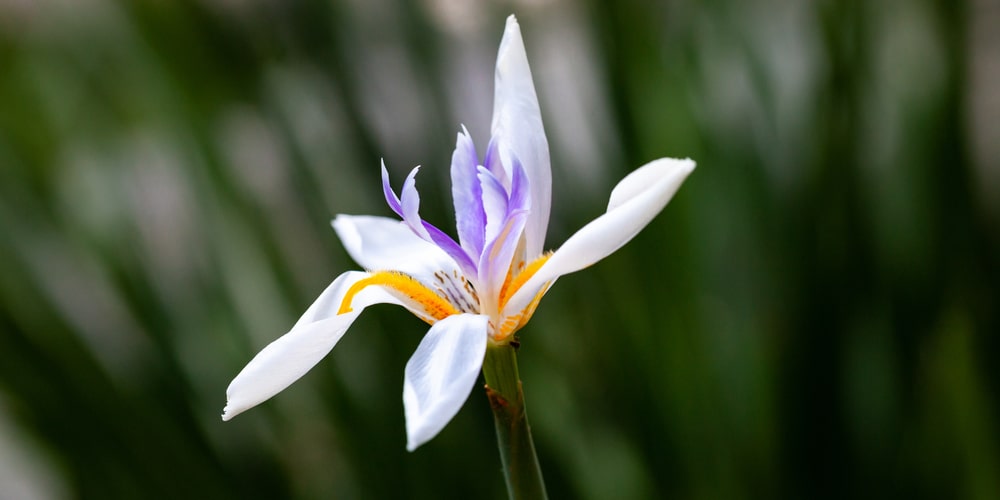
The White African Iris is a beautiful and delicate flower that is native to Africa. They are most commonly found in marshy areas or near streams and lakes. These flowers have a distinctively shaped petal that resembles the head of a lion. Each petal is intricately veined with bold streaks of white against a deep blue or purple backdrop.
Surprisingly, it thrives in hot, dry climates and is relatively drought-tolerant. It is also fairly easy to care for and is a low-maintenance plant.

| Botanical Name | Dietes Iridioides |
| Common Name |
White African Iris |
| Plant Type | Perennial |
| Flower Color | White with blue to purple and yellow markings |
| Size When Mature | 24 to 36 Inches |
| Bloom Time | Late Fall to Early Spring |
| Sun Requirements | Full Sun, tolates some shade |
| USDA Hardiness Zones | 8 – 11 |
| Soil PH Range | 6.1 – 7.8 |
| Soil Type | Rich, slightly acidic to alkaline, well-draining |
| Water Needs | Medium |
| Native Area | Eastern and Southern Africa |
What You Need to Know About White African Iris
The most important thing to remember is that these plants are poisonous. Skin irritation can occur if the sap comes in contact with the skin. When ingested, the plant itself is also toxic – making it unsafe if you have pets around.
This plant has an exotic smell that is slightly subtle. It has a powdery fragrance and might also have the scent of damp cement or the smell of a wet sidewalk after a thunderstorm.
One of the many beautiful features of this plant is its delicate and intricate flowers. Each petal is lined with bold streaks of white against a deep blue or purple. The plants can grow to be about 2-3 feet tall. This perennial plant blooms from late spring through early summer.
Despite its delicate appearance, the White African Iris is actually quite easy to care for and even a beginner gardener can do it.
How to Care for White African Iris
Here’s everything you need to know about growing and caring for a thriving White African Iris:
Light
This plant needs full sunlight in order to bloom properly. If grown indoors, it should be placed in a sunny window where it will receive at least six hours of sunlight per day.
If you notice the leaves beginning to yellow, that’s a sign that the plant is getting too much sun and should be moved to a shadier spot. Be sure to rotate your plant every few weeks so that all sides have an opportunity to receive sunlight.
Water and Soil Needs
They should be planted in soil that is moist but well-drained with a PH between 6.1 and 7.8.
These plants can tolerate drought but will bloom more profusely with consistent moisture. Water the plant deeply about once a week, or whenever the soil feels dry to the touch.
Temperature Requirements
White African Iris does best in USDA climate zones 8 to 11. It thrives at temperatures between 55 and 85 degrees Fahrenheit but can tolerate higher or lower temperatures for short periods of time.
Fertilizer
The best fertilizer to use on a White African Iris is a balanced 10-10-10 fertilizer formulated for flowering plants. It should be fertilized once in the spring, and once in the summer.
Common Diseases
The White African Iris is susceptible to a variety of diseases. Bacterial leaf blight is a common disease that causes the leaves of the iris to turn yellow and eventually die. Rhizome rot is another disease that can cause the roots of the iris to rot, which can lead to the death of the plant.
Crown rot is yet another disease that causes the crown of the plant to rot. A fungus called an ink spot can cause black spots to appear on the leaves of the iris, while a leaf spot is a fungus that causes brown or yellow spots to appear on the leaves.
Tiny creatures called nematodes can infest the roots of the iris and cause damage. Unfortunately, this plant can also be affected by a soft rot which is a bacterial disease that can cause the flesh of the iris to rot.
White African Iris Propagation
The African Iris can be propagated by seed or division. To propagate by seed, plant the seeds in a pot or container filled with potting mix. Water the potting mix until it is moist but not soggy. Place the pot in a warm location, such as on top of a radiator or near a heat vent.
Keep the potting mix moist by watering when necessary. The seeds will germinate in two to three weeks. Once the seedlings have two or three leaves, they can be transplanted into individual pots or outdoors into the garden.
To propagate by division, dig up an existing plant in the fall after it has finished blooming. Carefully remove the plant from the ground and Shake off any excess soil. Use a sharp knife or spade to divide the root ball into two or three sections. Replant the divisions immediately and water well.
Related article: Flowers That Bloom in May