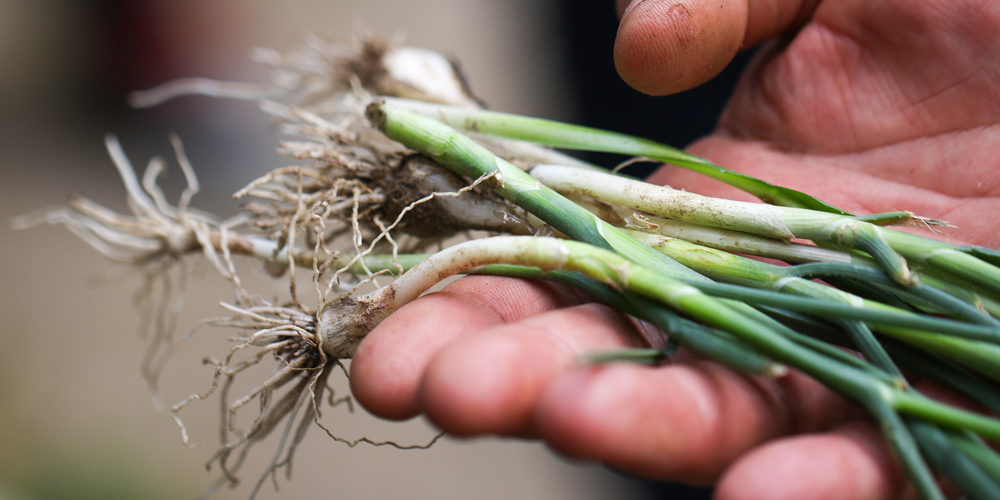
Garlic mustard and wild onions are spring ephemerals native to eastern North America. They’re easy to identify because both have triangular leaves with petioles (stalks) that attach near the middle of the leaf blade rather than at the base.
Wild garlic is a bulbous plant that grows in fields, meadows, and near the edges of forests. The leaves are broad with a smooth edge, and the flowers are white with six tepals (petals and sepals). They have a strong garlic smell.
Wild onion is also a bulbous plant, but it has a rounder shape than wild garlic. The leaves are slender and sharp-edged, and the flowers are pale purple or pink. They have a mild onion smell. Let’s compare wild garlic vs wild onion.
Wild garlic vs wild onion: How to Grow

Garlic Mustard
Mustard garlic tolerates a wide range of soil conditions but prefers a moist, well-drained site in full sun. It can be grown from seed or cloves planted in the fall.
Wild Onions
To propagate wild onions, break off a small piece of the onion and replant it in soil. The onion will grow new roots and shoots and eventually produce a new onion. You can also divide an existing clump of onions into several smaller clumps.
Wild garlic vs wild onion: When to plant
The best time to plant wild onion and mustard garlic in Georgia is typically in the fall, but there are variations depending on the climate and elevation of your region.
For the lower elevations of Georgia, late September through early November is the best time to plant. For the higher elevations, plant in late October through early December.
Do They Grow Well In GA?
Garlic Mustard
Garlic mustard is a biennial plant that is native to Europe and Asia. It was introduced to the United States in the 1800s as a food crop and an herb for medicinal purposes.
Garlic mustard can be found growing in disturbed areas, such as abandoned fields, forest edges, and roadsides.
Wild Onion
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best way to grow wild onions in Georgia will vary depending on your area’s specific climate and soil conditions.
However, some tips on how to grow wild onions in GA include planting them in sunny locations with soil that is well drained and harvesting them when they are young and tender.
Hardiness Zones
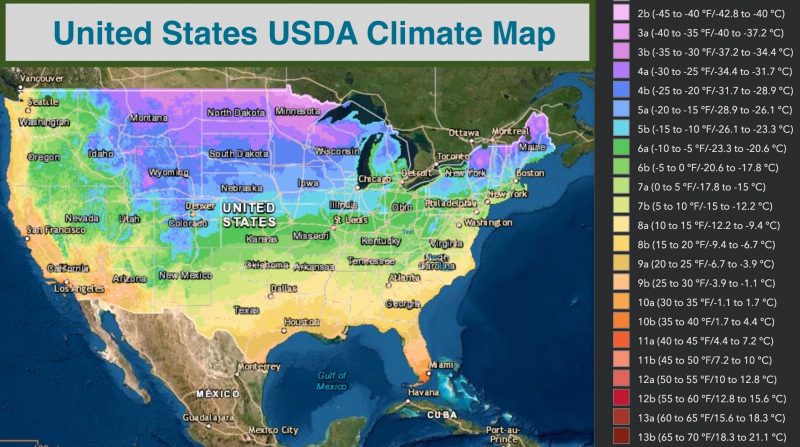
Garlic mustard is a hardy plant and can grow in USDA hardiness zones 6 to 8. It prefers moist, shady areas but can also grow in sunny locations. In contrast, the USDA hardiness zones for wild onions are 4 to 9.
Shrubs That Grow In Georgia That Provide Privacy
Georgia USDA plant hardiness zone is 6 to 9. Thus for any type of shrub to do well in this area, it should be within this hardiness zone. Here are a few shrubs that can do well in Georgia:
Ligustrum- This plant creates tall, dense foliage making it best for screening shrubs. Its USDA hardiness zone is 8 to 10.
Loropetalum- This shrub comes in different varieties of different sizes and flower colors. It’s a perfect shrub if you want to add color to your garden and its USDA hardiness zone is 7 to 10.
What Is Bolting?
Bolting is a plant’s response to environmental stress. It’s a very risky process, as the plant diverts all of its resources away from growth and the production of flowers or seeds.
This can be disastrous if the conditions that caused bolting are not long-term, as the plant may not have enough time to produce mature fruits or seeds before dying.
What to Do When They Bolt?
If you catch plants bolting early on, you can try to correct the problem that is causing the stress. This might mean watering them more often, adding fertilizer, or adjusting the temperature in the room.
You can also try to clip off the flowers and buds formed. This will redirect the plant’s energy back into growth. If any leaves have turned yellow or brown, you can also remove them.
Collard Planting Tips to Keep Them from Bolting
Collard greens are a cool-weather crop that can be planted in the spring or fall. They are a member of the cabbage family and are related to broccoli, kale, and brussels sprouts. Collards are a good source of vitamins A, C, and K. They also contain a high amount of fiber.
Pro tip: To avoid bolting in collard, avoid temperature extremes, water stress, and nutrient deficiencies.
Wild garlic vs wild onion: Conclusion
Wild garlic and wild onion are two plants that are often mistaken for each other. However, there are a few ways to tell them apart. The most obvious difference is the smell.
Wild onion has a strong onion smell, while wild garlic does not have a noticeable smell. Additionally, the wild garlic leaves are broad and flat, while the leaves of wild onion are thin and blade-like.
Related Article: When to Plant Garlic?